EBV+ Lymphoma may be associated with inferior survival outcomes.
Identifying which of your patients have EBV+ tumors may provide a new personalized treatment option.
Learn more about the NAVAL-1 clinical trial evaluating an oral, first-in-class, investigational combination therapy for patients with EBV+ lymphoma.

Lymphomas are the most common Epstein-Barr virus-positive (EBV+) cancers. There are currently no approved therapies targeting EBV+ lymphomas in the United States.
Incidence of EBV+ Lymphoma
EBV+ malignancies account for ~2% of all new cancer cases globally.
EBV Positivity* by Lymphoma Subtype1,5
EBV Positivity May Have an Adverse Impact on Clinical Survival Outcomes2-6
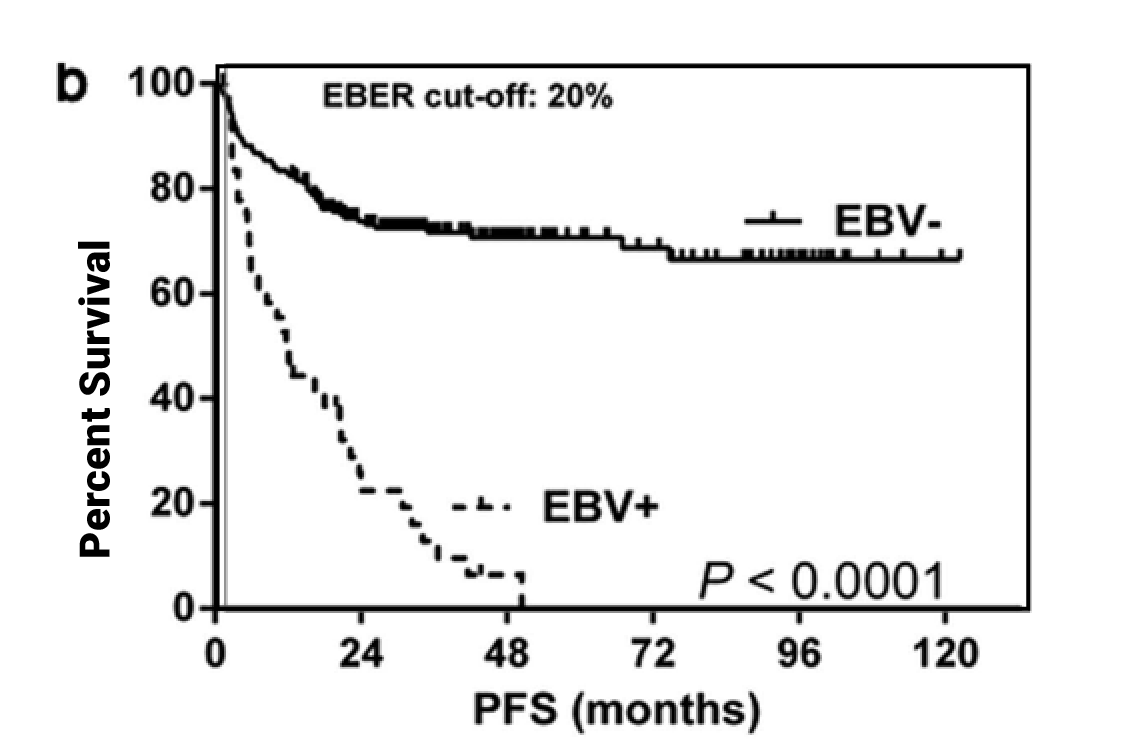
DLBCL
(Progression-Free Survival)
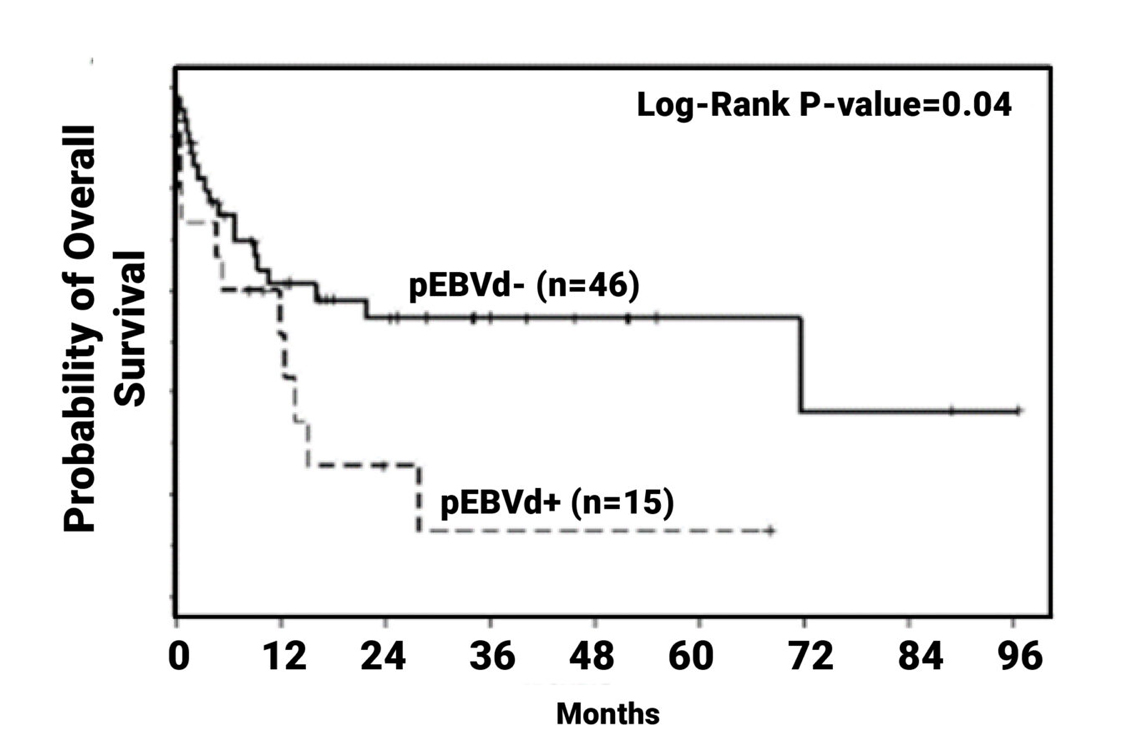
PTCL
(Overall Survival)
About the NAVAL-1 Clinical Trial
The NAVAL-1 clinical trial is a global, pivotal phase 2, multicenter, open-label, single-arm basket study designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the all-oral combination of nanatinostat with valganciclovir in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) EBV+ lymphoma. The trial will evaluate multiple subtypes of EBV-associated lymphoma (PTCL; DLBCL; PTLD) with an additional cohort that will capture patients with other types of EBV+ lymphoma.

The Investigational All-Oral Drug Combination: "Kick and Kill” Mechanism of Action
The NAVAL-1 clinical trial represents a novel approach to the treatment of EBV+ lymphoma, using a combination of an oral class-I specific HDAC inhibitor (nanatinostat) with an oral antiviral (valganciclovir, an oral prodrug of ganciclovir).
- EBV exists in a latent form in tumor cells. In that form, it is not susceptible to the cytotoxic activity of ganciclovir.
- Nanatinostat induces EBV lytic activation and expression of the EBV BGLF4 protein kinase (the “Kick”).
- This in turn activates ganciclovir via phosphorylation, resulting in ganciclovir-induced inhibition of viral and cellular DNA synthesis and apoptosis (the “Kill”).
Nana-val “Kick and Kill” Mechanism of Action

LATENCY
EBV latent in cancer cells.
Valganciclovir, antiviral prodrug of ganciclovir (GCV), is inactive without expression of viral protein kinase (PK)
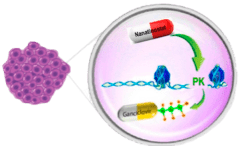
THE KICK
Nanatinostat selectively and potently induces expression of EBV protein kinase (PK), which activates GCV into its cytotoxic form
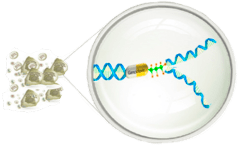
THE KILL
Cytotoxic GCV inhibits DNA replication leading to apoptosis in EBV+ cancer cells

Phase 1b/2 Study
In a previous Phase 1b/2 study, the combination of nanatinostat and valganciclovir was evaluated in 55 patients with a variety of relapsed/refractory EBV-associated lymphomas. Eligible patients had received 1 or more prior therapies, had measurable disease, and had exhausted all standard therapies.1
The regimen was generally well tolerated: the most common treatment-emergent adverse events were nausea (38%); thrombocytopenia (36%); neutropenia (34%); anemia and constipation (both 31%); creatinine elevation, diarrhea, and fatigue (all 26%); and decreased appetite (22%).
For the 43 evaluable patients, the ORR was 40% (CR 19%). Complete responses were reported in DLBCL, T- and NK-cell lymphomas, and IA-LPD, with a median duration of response of 10.4 months.
This investigational drug combination received FDA fast track designation for the treatment of R/R EBV+ lymphoid malignancies in 2019. In addition, this drug combination received 4 orphan drug designations from the FDA for plasmablastic lymphoma; PTLD; T-cell lymphoma; and EBV+ DLBCL, NOS.
NAVAL-1 Phase 2 Basket Study in Patients With R/R EBV+ Lymphoma
Key Eligibility Criteria
- Adults ≥ 18 years
- EBV+ relapsed/refractory lymphoma following 2 or more prior systemic therapies
-
For PTCL patients only: Relapsed/refractory disease following 1 or more prior systemic therapies. No available therapies in the opinion of the Investigator
-
- Not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy with allogeneic/autologous stem cell transplantation or CAR-T therapy
- No CNS involvement
-
Adequate hematological and hepatic function
NAVAL-1 Phase 2 Basket Study Design
This global clinical trial is seeking to enroll multiple subtypes of patients with EBV+ relapsed/refractory lymphomas, with a fourth cohort included for patients with other types of EBV+ lymphoma.
Stage 1
Multiple EBV+ lymphoma subtypes
Stage 2
Stage 1
Multiple EBV+ lymphoma subtypes
Stage 2
Participants Who Qualify and Enroll Will Receive:
- The investigational oral drug combination and all study-related medical care at no charge
- Close monitoring by physicians who specialize in virus-related lymphomas
- Reimbursement for study-related expenses such as transportation (as needed)
- The opportunity to advance medical knowledge of EBV+ lymphomas
Take Action
Ask questions about the trial and see if your patients may qualify:
clinicaltrials@viracta.com
For more information about the trial visit:
Clinicaltrials.gov
NAVAL-1 National Trial Reference Number [NCT05011058]
Phase 1b/2 National Trial Reference Number [NCT03397706]
US Trial Locations
References
- Haverkos BM, Alpdogan O, Baiocchi R, Brammer JE, Feldman TA, Capra M, et al. Nanatinostat (Nstat) and valganciclovir (VGCV) in relapsed/refractory (R/R) Epstein-Barr virus-positive (EBV+) lymphomas: final results from the Phase 1b/2 VT3996-201 study. Blood. 2021;138 (suppl 1):623. doi:10.1182/blood-2021-152603
- Lu, T, Liang J, Miao Y, et al. Epstein-Barr virus positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma predict poor outcome, regardless of the age. Scientific Reports. 2015;5:12168. doi:10.1038/srep12168
- Haverkos B, Huang Y, Gru A. Frequency and clinical correlates of elevate plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA at diagnosis in peripheral T- cell lymphomas. Int J Cancer. 2017;140(8):1899-1906. doi:10.1002/ijc.30566
- Dupuis J, Emile J, Mounier N, et al. Prognostic significance of Epstein-Barr virus in nodal peripheral T-Cell lymphoma, unspecified. Blood. 2006;108(13)4163-4169. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-04-017632
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. World Health Organization; 2017
- Mackrides N, Champman J, Larson M, et al. Prevalence, clinical characteristics and prognosis of EBV-positive follicular lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(2):E62-E64. doi:10.1002/ajh.25357
